One of the frequently asked questions from our readers is: can a plasma cutter cut aluminum? Well, plasma cutting machines have come a long way since the late 1990s, which is the period many people think of when referencing plasma cutters.
Plasma cutters now have the latest technology that easily allows them to cut through any type of conductive metal.
Can a plasma cutter cut aluminum? Aluminum falls into the category of being a conductive metal and, therefore, is easily cut by a plasma cutter if it’s less than six inches thick. Plasma cutters can cut through most conductive metals, but it becomes harder the thicker the metal is.
Many people fail to realize how far plasma cutting technology has progressed in the past decade alone. This plasma cutting guide of sorts will give you knowledge of how plasma cutters work and their potential applications, which can save you lots of money and time when conducting projects.
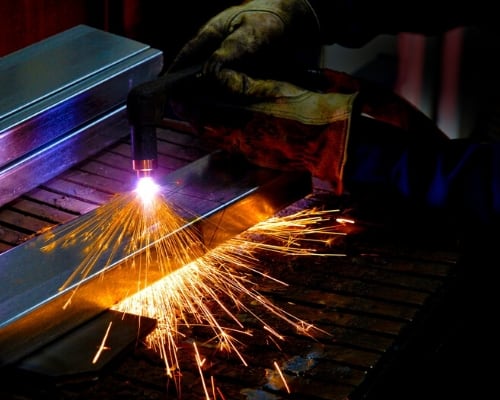

Table of Contents
How Plasma Cutter Cuts Aluminum
Plasma cutters cut aluminum, along with other conductive metals, by using a concentrated stream of ionized gasses. Common types of metals plasma cutters can cut through include:
- Mild Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Brass
- Copper
- Cast Iron
- Other types of metal alloys
Plasma cutting works by using ionized gasses. The ionized gas has more protons or positive ions than it usually would in nature, making it super-heated. It changes into another state of matter called plasma.
It is the interaction between the plasma protons and the metal that allows plasma to cut through conductive metals.
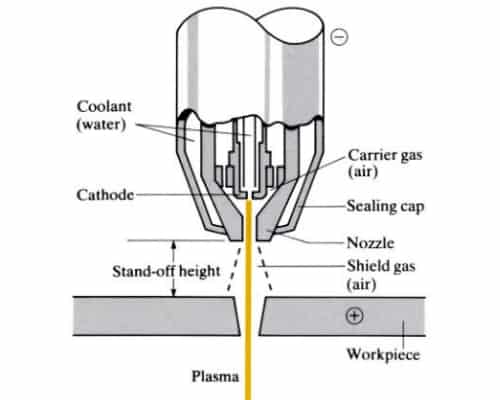
The protons are attracted to the conductive metal, which has a slightly positive charge, much like the opposing poles of a magnet. When the plasma gas comes into contact with the metal, the electrons from the plasma are transferred to the metal.
Being in an ionized state means that the electrons can freely move between the atoms of the gas and to the metal. The transfer of these electrons creates heat energy and essentially melts the metal that it comes in contact with. The melting of the metal creates a clean, uniform cut through the metal.
Plasma Cutting Basics
The basics of plasma cutting are essential to know if you want to experience the money and time-saving process that is plasma cutting. Other than the exact plasma cutting science previously mentioned, you must also understand a few more things about the plasma cutting process.
The Gas
The two gases which are used in Plasma Cutting are oxygen and Nitrogen. Both of which have to be almost 100% pure, or at minimum 99.5% pure for oxygen and 99.995% pure for Nitrogen. The consequences of using any less purity gas than recommended are:
- that the arc losses its ability to cut through metal at any current level.
- that the arc develops variation in the cut quality.
- that the electrode that ionizes the particles is considerably shortened.
- that when cutting with Nitrogen, a black film appears on the electrode and in the nozzle.
A process called gas swirling is utilized in many plasma cutting machines because of the benefits that it provides in the process. The process works by using the fact that only 30% of the gas is ionized, leaving 70% of the gas non-ionized.
The non-ionized gas is significantly cooler in temperature compared to the ionized particles. The machine swirls the gas to allow the mixture of the ionized and non-ionized particles.
The non-ionized particles act as a temperature barrier to protect the copper alloy nozzle from melting.
Learn More About Plasma Arc Machining – PAM – Here, you can find an article from our website about: The Advantages and Limitations of Plasma Arc Machining?
The non-ionized particles also serve another purpose that is necessary for the clean, precise cut of the plasma cutter. The non-ionized particles blow away all the molten metal from the cutting area.
This allows the plasma arc to keep in constant, even contact with the metal surface without anything getting in the way.
The swirling of the gas evenly spreads the ionized particles all the way through the arc. The benefit of which allows for a tremendously even cut all the way through your cutting piece.
Overall, the breakthrough of utilizing the concept of swirling the gas gives numerous benefits that were not previously seen in the early ages of plasma cutting.
The Nozzle
The nozzle of the plasma cutter is a vital part of the plasma cutting system. It concentrates the plasma arc cutting stream, much like the nozzle on a water cutting system. The nozzle is responsible for the size, power, and angle of the cut you make.
The nozzles are typically made of a copper alloy because of its heat retention properties and electrical conductivity properties. The copper nozzles are protected from the majority of the heat created by the plasma arc by a process called gas swirling.
The gas used for plasma cutting is not fully ionized. In optimal conditions, roughly 30% of the gas is ionized, leaving 70% of the gas in a non-plasma state, as mentioned before.
Related Article: What Are Metal Welding Nozzles Made Of? | Understanding MIG Welding Nozzles
There are many types of nozzles you can use on your plasma cutter that have a range of orifices. The size of the hole is vitally important because it is what determines the size and the voltage of your arc. The smaller the hole, the larger the arc and voltage are.
You would want a smaller orifice when you are cutting:
- tougher metals
- thicker metals
- Less conductive metals
The higher the voltage, the higher the temperature the nozzle is subjected to by the ionized gas particles. Each nozzle has a maximum temperature it can withstand on the packaging of the nozzle.
If you exceed the maximum temperature, your nozzle can melt, or it significantly reduces the lifespan of your nozzle.
Benefits of Plasma Cutting
There are many benefits of plasma cutting over any other form of cutting, especially in today’s time.
When people rule out plasma cutting for projects, they are commonly stuck in the mindset of the 1980s to the 1990’s age of plasma cutting, which was barbaric when compared to the technology of today.
Plasma cutting technologies have been able to increase the ability from plasma to be able to cut through an inch of metal to now being able to cut up to six inches of the metal relatively quickly.
The development of swirling the gas and others has led to being able to increase the current levels and arc size of the plasma cutter significantly.
Another form of cutting metal is oxy-cutting, which has a minimal amount of metals it can cut. Oxy-cutting can only cut through metals that oxidize, which severely limits the metals it can cut.
The technological breakthroughs that have been occurring with plasma cutting have made the ability to use the cutting platform cheaper, more cost-effective, and faster.
Can a CNC Plasma Cutter Cut Aluminum?
Yes, a CNC plasma cutter can cut aluminum. However, it is important to note that not all aluminum alloys can be cut with a plasma cutter, and some may require a water table.
It is also recommended to use a high-quality plasma cutter with durable performance and high-powered flexibility, such as the ACCURL CNC Plasma Cutter Machine.
It has an aluminum cut capacity listed in the cutting data table and can be upgraded to faster speed and high-definition plasma options as the business grows.
How Thick of Metal Can a Plasma Cutter Cut?
Plasma cutters are capable of cutting different thicknesses of metals, depending on the type of plasma cutter used. Handheld plasma cutters can cut through mild steel up to 1.5 inches thick, while industrial plasma cutters can cut through steel up to 6 inches thick.
For thicker metals, oxy/fuel cutting technology can efficiently cut metals up to 24 inches thick. Nevertheless, it is important to note that the thickness of the metal is not the only factor that affects the cut’s quality.
The type of metal being cut also plays a role in the cut’s quality. Plasma cutters can cut through many different metals, including mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and titanium.
How Many Amps Does It Take To Cut Aluminum With Plasma?
Plasma cutters can cut aluminum with a machine that is packed with 45 to 260 amps. However, the thickness of the aluminum being cut affects the amperage required. For aluminum up to 160mm, a plasma cutter can be used.
It is important to note that certain alloys may require a water table and a high-quality plasma cutter is recommended for the best results. Additionally, while plasma cutting is effective for cutting aluminum, oxy/fuel cutting technology is better suited for thicker metals.
Why Is Aluminum So Hard To Cut?
Aluminum can be difficult to cut because of its low melting point. When using plasma cutters to cut aluminum, a proper gas mixture, nozzle, and settings are required.
Industrial plasma cutters can cut through steel up to 6 inches thick. However, oxy/fuel cutting technology is better suited for thicker metals. Certain alloys may require a water table, and a high-quality plasma cutter is recommended for the best results.
What Gas Do You Use To Plasma Cut Aluminum?
The gas mixture that is mostly used to cut through aluminum is argon-hydrogen. Argon-hydrogen mixture produces the hottest plasma cutting flame and some of the cleanest cuts, making it ideal for cutting through stainless steel and aluminum.
The appropriate amount of amps required for plasma cutting aluminum depends on the thickness of the aluminum being cut. Generally, for aluminum, the recommended range of amps is from 45 to 260.
Certain aluminum alloys may require a water table, and oxy/fuel cutting technology is better suited for thicker metals
The Future of Plasma Cutting
The future of plasma cutting will, undoubtedly, be bright. The recent technological advancements have widely focused on the accessibility of plasma cutting platforms.
Recent innovations in the ability to control the power and size of the arc have led to plasma cutting being used for more complex cutting projects.
The technology advancements also have led to better accuracy when cutting and a more uniform cut through the metal not seen in the early days of plasma cutting.
The next step, which is already taken hold in the plasma cutting industry, is automation and bringing that automation out of purely industrial areas to the average person who uses plasma cutting systems.
This process involves making the parts of the machines last for more extended periods and the reduction of the price of these parts.
The process of using plasma cutting has undeniable benefits compared to other ways of cutting through metal and is no longer tainted by the early, barbaric, plasma cutting platforms.
Recommended Reading
Can MIG Welders Weld Aluminum? | How to successfully weld Aluminum?
What are the Advantages and Limitations of Plasma Arc Machining?
How to Weld Aluminum at Home >> A Beginner’s Guide
Plasma Cutter Cutting Aluminum >> Tutorial video

