As welding begins to be on high demand, there are many types of welding opportunities. From helping major corporations in handling simple freelance tasks, welding has been a career choice suited to provide structure and maintenance whenever possible. With that said, there is something that not many seem to know about in the field of welding: 4G weld testing and certification.
What exactly is 4G weld testing? 4G weld testing is a type of welding procedure and certification that allows a welder to perform in order to increase his skills and abilities as a welder. With this certification, the welder can now be able to handle the process of groove welding, a type of welding that enables the metal to be joined together in an overhead position.
By learning more about the process of 4G weld tests and certification, it can allow us to understand the positions/formats in which many welders use during their careers and services. It can also perhaps provide an impact to many starting welders and increase the high demand for the career moving forward.
Table of Contents
What Is A 4G Weld Test?
A 4G weld test is a type of welding test that enables welders to obtain certification. What 4G weld in general covers is the position of which the welders can perform his welding services and get the job done. In fact, in the world of welding, there are at least four types (in which the number 4 comes from) of positions that welders must master:
- 1: Flat
- 2: Horizontal
- 3: Vertical
- 4: Overhead
With this key in mind, what 4G mainly covers is Overhead Groove Welding. Meaning, the ability of welding metals to be joined together in an overhead position. Since this is the fourth, that most likely means that it is the hardest to do from the rest of the welding positions. More on what they are will be mentioned down below.
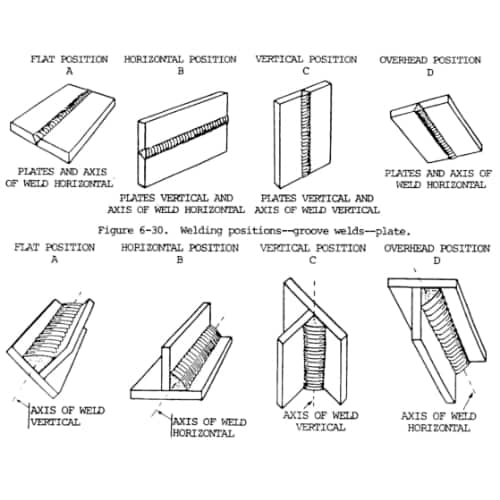
What Are Welding Positions?
Since welding is a tough career when it comes to application, it is important to understand the type of wedding positions, which were mentioned briefly above. Here, we will go over each of them in more detail in order to further understand what the 4G weld test is for many welders who will take it.
For these four positions, there are two categories that each welder gets tested on:
- Fillet (F): welding two metals into a perpendicular angle. They are shaped like the letters T and L. They are shaped triangularly and used to connect pipes.
- Groove (G): welding two metals through the middle so that they are joined together in the process. They are squared shaped and usually flat compared to the fillet weld.
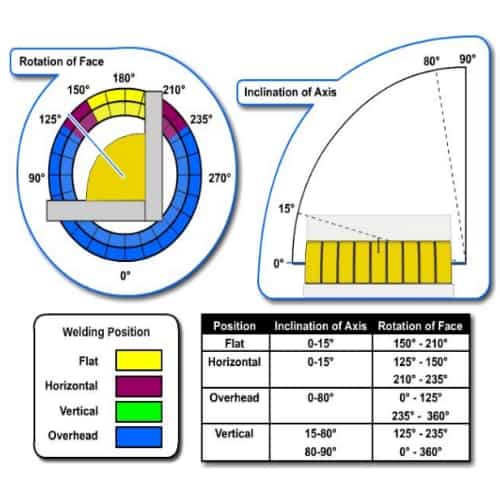
Flat Welding Position
The flat positions are the easiest of the four types of positions for welders to get tested on. What this position does is that the welder must have both plates and the axis weld in a horizontal position in order to let gravity do its job for the molten metal. The process is the same for both 1F (Flat Fillet) and 1G (Flat Groove).
Horizontal Welding Position
Horizontal positions are similar to the flat when it comes to the position of the axis of the weld being horizontal. However, the plate must be in a vertical position in order for the molten metal to flow down. This position is harder when it comes to the molten lava than the flat position.
Vertical Welding Position
Vertical positions require a lot more force against gravity when it comes to using the molten metal. In this position, the welder must have the molten metal be pushed either in an upward or downward position.
Upward allows the welder to use the flame being used at a 45-degree angle, allowing the welding to done while going against gravity. In the downward position, metal from the upper parts and its kinetic force is being used.
Overhead Welding Position
Overhead is the one that is what this topic is about and is the most complicated position to weld. In this position, the welding is carried from the underside portion of the join being made.
The metal is deposited to the joint and sags there, resulting in a bead-like shape, to which welders must prevent during the process. What welders do is keep the molten metal in small portions. If the molten metal expands, the welder must remove the flame in order for a cooldown to begin.
Passing The 4G Weld Test
Once a welder passes the 4G weld test or certification, that means the welder can now operate overhead positions for welding projects. Since welding is an easy career to study, but rigorous in training, it is important to note that passing this test requires a few key tips and tricks.
With these tricks, you can pass the test easily and perform this welding position effortlessly. It can also save your life and protect you from any possible harm and damage.
Tip #1: Positioning Is Be Similar To 1Gs
It is recommended that the position you are in should be one similar to one being used in the 1G testing. Welders use this tip as they understand that the process of a 4G weld is the same as a 1G weld, except it is done upside down. The same is dealt with the electrode angles, the travel speed, and even amperage.
Tip #2: Find A Comfortable Position
By finding a comfortable position to work with the welding during the 4G test, it can enable you to work with the molten metal easier. Welders who have taken this test have preferred that during the test, the welder should be in a position that is comfortable enough to see the puddle of the molten metal rather than the arc.
This can be said with the way you position your rod and the stand you use when performing the 4G welding test.
Tip #3: Using The Rod Efficiently
Sometimes there can moments during the 4G welding test that can cause some major if not severe burn injuries in your palms, knuckles, or hands. Of course, it is highly recommended to wear gloves since you are playing with serious flames, the way in which the welding rod should be positioned is in a manner that doesn’t cause burn damage to your hands. This allows the work to be done efficiently and not cause any further burns in your hands.
Tip #4: Position Your Feet Carefully
As well as the possibility of causing burn damage to your hands, the same can be said with the positioning of your feet when taking the 4G welding test.
Much like how you want to position your rod in a manner that doesn’t burn your hands, your feet should be in a position that can allow the lead of your welding rod to be utilized to its fullest. If your foot happens to step on the lead of the rod, it can cause you to lose your balance.
Tip #5: Wear Protective Gear
Like lawyers wear suits for their business meetings or firefighters wearing their fire gear, welders also have a uniform when working. For many welders, they utilize flame-proof upper wear that covers their whole upper area as well as gloves for their hands in case any bouncing flames appear during the process.
Welders also wear face masks and additional working goggles or glasses that can allow them to see through the sparks and flames and perform the welding with efficiency and care.
4G Stick Plate Welding Open Root >> Check out the video below

