Have you ever wondered what are the differences between plasma cutter and oxy-acetylene torch cutter? Welding metals can be accomplished with a range of heating techniques to join or separate these strong materials. Torch welding, or oxy-acetylene welding, and plasma cutters are two of the ways in which you can cut and manipulate metals. Comparing the two techniques will give you the best information in choosing which method is more ideal for your welding applications.
What are the key differences between Plasma cutter and Oxy-acetylene torch cutter? Oxy-acetylene Torch cutter uses the combustion of gases to melt metals while plasma cutting combines electricity with gas. If you value clean and precise lines, a plasma cutter is a better option. If you are looking for a more versatile tool that you don’t need a power source to operate, torches could be more beneficial.
| Creation of heat source | Oxy-acetylene uses combustion of gases to melt metals while plasma cutting combines electricity with gas |
| Material applications | Torches can cut through thicker metals than plasma cutters |
| Cutting precision | Plasma cutting often results in cleaner and faster cuts |
| Portability | Oxy-fuel is typically more portable without a need for electricity |
| Versatility | Both methods offer unique usage and applications |
While both methods are satisfactory for cutting metals, one method may be preferred over the other depending on the type of metal used as well as your preference on the details mentioned above. We will detail each of these categories, offering the advantages and differences between torch and plasma cutting as well as the technical configurations of both.
Table of Contents
Differences Between Torch and Plasma Cutters
Let’s first cover the technical differences between the two processes that are used to cut metal as well as achieve a variety of metal manipulation techniques. The processes will require different equipment and materials to perform. Understanding the steps in performing each will note their differences and allow you to tackle both methods for metal cutting.
How Does Torch (Oxy-acetylene) Welding Work?
The oxy-fuel welding method combines oxygen and a gas (typically acetylene) to create a very hot flame that can cut through metal. The oxygen and acetylene levels can be adjusted on the torch to create the ideal flame for cutting metal or fusing metals together. In the context of comparing torches to plasma cutting, we will focus on the cutting capabilities of a torch.
Related article: Here, you can find an article from our website about the topic: Is Welding Oxygen the Same as Medical Oxygen?
To cut metal with a torch, you will need to follow these steps and directions:
1. Acquire materials: You will need an oxygen tank, acetylene tank, and a torch. The tank size will depend on the amount of welding you plan to do, with larger tanks being more economical over frequent use. Appropriate hoses attach the tanks to the torch.
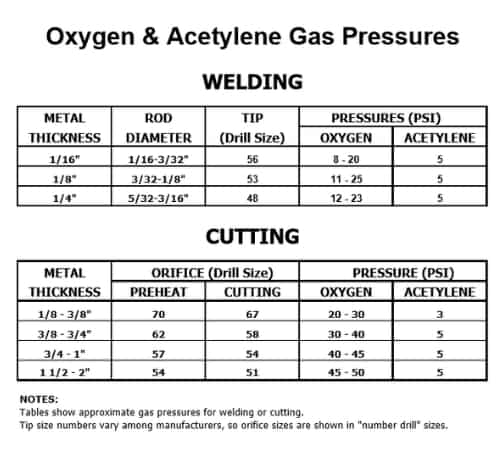
2. Open gas tanks: The thickness of the metal will determine your oxygen and gas pressures (as well as the tip you use on the torch). This helpful guide will give you the appropriate levels for both. Both need to be opened and set to send ample fuel and oxygen to the torch.
3. Start torch: Open the acetylene knob on your torch first and let any black smoke burn off. Then introduce your oxygen to create a precise flame. You will want a neutral flame for the best cut, which includes 50% oxygen and 50% acetylene. You will see small cones that should be equal when the oxygen lever is used.
4. Preheating metal: In oxy-fuel welding, you will need to preheat the metal before cutting. You will want to bring the specific metal up to its kindling temperature before cutting to prevent cracking.
5. Begin cut: Pressing the oxygen lever all the way down, move slowly and precisely with the torch across the ideal cutting area. Try to keep your torch as steady as possible to perform an even and straight cut.
The primary principles of this welding method are that you need oxygen and a fuel source in order to cut through the metal. Preheating is required for this cutting to take place, and you should be using a neutral flame for the best results. The materials that can be cut during this process must contain some form of iron to be oxidized in torch welding. Check out the video below
How Does Plasma Cutting Work?
In plasma cutting, you can work on a wide variety of materials as long as they can be electrically conducted. This process requires an electrical source, compressed air, and a metal workpiece. Using the electrical arc created by your power source and the added gas (air) will create plasma when put through a small nozzle in the plasma cutting torch.
Compared to the oxy-fuel process, the creation of this plasma flame is significantly higher in temperature, which allows for faster cutting. You do not need to preheat the metal because of this higher temperature, but you will also need an electrical power source, unlike in oxy-fuel welding.
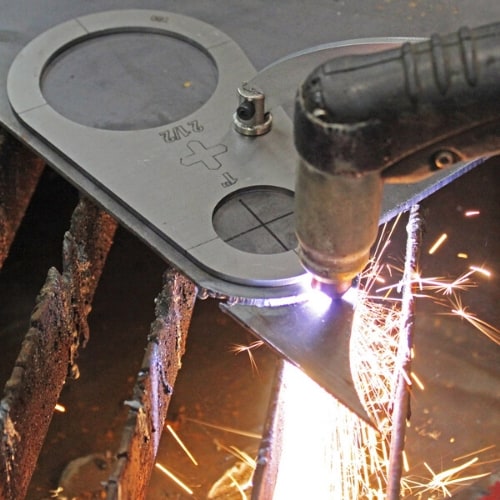

The process of cutting metal with a plasma cutter is much different oxy-fuel process, which is described in these steps:
1. Acquire materials: Use a gas or air source (shop air is common) and a plasma cutting machine. This machine must be attached to a power source to use and has an attached torch for your cutting actions. Separate air compressors are hooked up to the torch for best results.
2. Turn on air compressor: This will allow the necessary pressure to build. Look at your specific user guide for the needed air pressure and amperages as they vary from machine to machine.
3. Use ground clamp: Because you are conducting electricity, using a ground clamp and attaching it to the piece of metal will ensure the cycle of electricity does not injure you.
4. Connect air and plasma cutter: You will want to make sure that the torch and air are securely connected to the plasma cutting machine.
5. Begin cut: Hold down the button to turn the torch on. Keep torch close to metal piece but without touching for cleanest results. Move across quickly in one smooth motion until you work through the entire piece of metal.
In the plasma cutting process, your cuts will often be more efficient and faster, with no need to preheat or manipulate multiple gases. Preparing the air compressor beforehand will ensure you have enough air pressure to complete the cuts. Be careful in this process and wear protective equipment as sparks are created.
Additional Differences Between Oxy-acetylene Torch and Plasma Cutter
As detailed above, the largest difference between the two metal cutting processes is the equipment used and how this impacts the cut that is completed. In torch welding, a chemical reaction is occurring between the fuel source, oxygen, and metal. In plasma cutting, electricity and gas work in a confined area to produce a fourth state of matter.
Beyond the varying processes, these are important differences between the two welding methods:
- Metal compatibility: Torch welding can only be used on ferrous (metals containing iron) metals, while plasma cutting works on metals that can be electrically conducted.
- Power: Your plasma cutter will need an electrical power source to work, unlike torch welding. This impacts portability and working on any type of job site.
- Efficiency: Plasma cutters can work through metals much more quickly than torches can, but these must be thinner pieces to work with.
The advantages of each type of cutting we detail in the next section will delineate between the two methods even more clearly and explain why you may want to use one over the other.
Learn More About Plasma Cutter – Here, you can find an article from our website about: The Difference Between a Laser Cutter and a Plasma Cutter?
Advantages of Using Oxy-acetylene Torche to Cut Metal
Torch welding is one of the most popular and trusted ways to cut metal because it can be done from nearly any location and work through a wide variety of materials. We have pulled together the key advantages of using a torch over a plasma cutter for metal cutting and manipulation.
Ability to Cut Thicker Metals
The strong supply of fuel gas and oxygen combust to create a very powerful flame that is capable of cutting through thick pieces of metal. One of the most useful applications for this is to work through steel, which can be more difficult to cut through than a variety of other metal types. Oxy-fuel welding can be efficiently used on metals that are up to 24 inches thick.
Your plasma cutter will not be able to work through these thicker materials with much success. They are typically more efficient and preferred for thin pieces of metal. If you have to choose between the two to work on a larger variety of metal workpieces, the torch will cut through a much greater variety of thicknesses.
At the same time, you may be compromising the quality of the cut on thinner metal when using a torch. We will go into more detail about this as we point out the advantages of a plasma cutter.
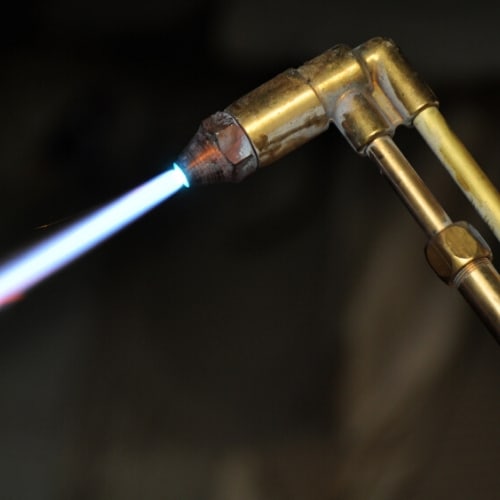

Increased Portability
Because you only need your oxygen and fuel source tanks to power the torch, you can use the oxy-fuel welding method anywhere. This is particularly helpful if you are on a job site or need to work with metals in remote locations. You can easily transport the tanks (with smaller tanks being easier to move) to your needed location for a variety of applications.
This cannot be said of the plasma cutting method, which will require a power source to be used. The electrical component to using a plasma cutter does place some limitations on where you will be able to cut metals. The primary workaround for this is to have a generator available to you. This is often common on a job site but may not be feasible in all locations.
For the overall ability to transport and use these systems anywhere, torch welding wins hands down. You don’t have to worry about adding a strong enough power source or having ample compressed air.
When transporting your gas cylinders, you will want to make sure you do so safely. These are a few things to keep in mind when transporting acetylene tanks:
- Keep them upright: When possible, keep your tanks upright to maintain the proper balance between the gas elements. If a tank must be stored horizontally, you will want to allow the tanks to return to their upright position for at least 30 minutes so the materials can properly reintegrate before use.
- Secure them: If tanks are not secured, especially in a vehicle, they could accidentally open valves upon contact with one another and pose a risk of fire.
- Ventilate: Make sure there is access to ventilation when transporting in the event of a leak. This can lead to a risk of fire or explosion, especially over extended periods.
Versatility in Usage
Cutting is not the only useful application for an oxy-fuel torch, as you can apply a wide variety of metal manipulation techniques. This makes it a smart investment if you plan to work with metal in various ways.
Some of the primary applications for an oxy-fuel torch beyond cutting include:
- Welding: This is the process of melting a base metal to join or adhere to two pieces of metal together. Torches are most commonly used for this process.
- Brazing: Torches can be used to melt a filler that will serve as the joint between two or more metals.
- Soldering: This process is similar to brazing but is done so at a lower temperature. Soldering melts filler metals below 450 degrees Celsius while brazing melts them above.
- Gouging: You would use gouging to remove metal by applying a significant heat source.
- Bending: Bending metal can be accomplished by heating and softening the workpiece without slicing through the metal.
The range in applications makes using a torch a helpful and suitable tool to have at your workstation. Plasma cutters are not as successful in doing many of these tasks because their temperature output is significantly higher (over 20,000 degrees Celsius), and they do not use filler metals to complete tasks.
Advantages of Using Plasma Cutters to Cut Metal
Plasma cutting has become a popular alternative to oxy-fuel welding because of the many benefits it provides in precision and efficiency. Let’s look more closely at the advantages of using plasma cutters over torches for cutting metal.
Cutting Precision and Speed
The extremely high heat and precision of a plasma jet through a plasma cutter make it an ideal choice for working on projects that need really clean lines. The increased speed at which the plasma cuts through the metal compared to a torch allows the line to be smooth and precise. This is important in applications where visual presentation is valued, such as art or architecture.
The plasma cutter is easy to manipulate and move, allowing you to cut interesting shapes and designs out of your metal pieces. This would be much more difficult with a torch that leaves less precise line due to excess heat. If you are looking to make very thin or fine lines to cut your metal, we recommend choosing a plasma cutter.
Related Article: What are the Advantages and Limitations of Plasma Arc Machining?
The quickness and precision of a plasma cutter is its most significant advantage and why metalworkers prefer it over a torch system. Plasma cutters are preferred in cutting stacked metals and shaping metals, especially with on thinner workpieces. You will also find it easier to use a plasma cutter for expanded metals than a torch alternative.
No Preheating Required
If you don’t want to rely on having ample preparation time before you begin your cuts, plasma cutting will be the preferred choice. Unlike oxy-fuel cuts, you do not have to preheat the metal before you begin. This makes it easy to set up the plasma cutter and work quickly, especially if you are working with many pieces of metal.
If you have a lot of metal pieces to cut, the plasma cutter will be more productive and efficient over time.
Non-Ferrous Metal Cutting
Plasma cutters can often be a more versatile and preferred option when it comes to cutting different types of metals. The only requirement to cut metal is that it can be electrically conducted. Unlike oxy-fuel torches (which require ferrous metals for chemical reaction), plasma cutters can work through stainless steel and aluminum.
If you plan to work with either of these materials, a plasma cutter will be your optimal choice. There are many metals you can use in plasma cutting, all having the ability to conduct electricity. The most common metal applications for plasma cutting include aluminum, steel, and stainless steel.
Choosing an Oxy-acetylene Torch vs. Plasma Cutter
Laying out the different processes and the advantages between the two systems, the preference largely depends on your metal application. The type of metal (ferrous vs. nonferrous) and the thickness of the workpiece will be your first indicators as to whether you should use a torch or a plasma cutter.
The key to choosing either metal cutting method is to do so safely. Ensure you have all the necessary equipment to get the job done, which includes personal safety equipment and an organized workspace in the event of an accident. Emphasizing safety will not only minimize danger but will allow for more careful and accurate cutting practices.
sources:
linde-gas.com
twi-global.com/technical-knowledge
tibtech.com/conductivite.php
grainger.com/content/supplylink-great-debate-cutter-or-torch
Recommended Reading
What Is the Difference Between a Laser Cutter and a Plasma Cutter?
What are the Advantages and Limitations of Plasma Arc Machining?

